std::vector in C++
Master std::vector in C++: Efficient dynamic arrays with fast access and versatile operations.
Introduction to std::vector
C++ is a powerful programming language widely used in software development. One of its most essential components is the Standard Template Library (STL), which includes the versatile std::vector. This dynamic array can grow and shrink in size, providing a flexible way to manage collections of data.
What is std::vector?
std::vector is a sequence container in C++ that allows dynamic resizing. Unlike arrays, which have a fixed size, vectors can expand or contract as needed. This flexibility makes std::vector a popular choice for storing collections of data.
Key Features of std::vector
- Dynamic Size: Can grow or shrink as needed.
- Contiguous Memory: Elements are stored in contiguous memory locations, enabling efficient access and cache performance.
- Automatic Memory Management: Handles memory allocation and deallocation automatically.
- Range Checking: Provides at() function for bounds-checked access.
How to Declare and Initialize a std::vector
Here are some basic ways to declare and initialize a vector:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main() {
std::vector<int> vec1; // Empty vector of integers
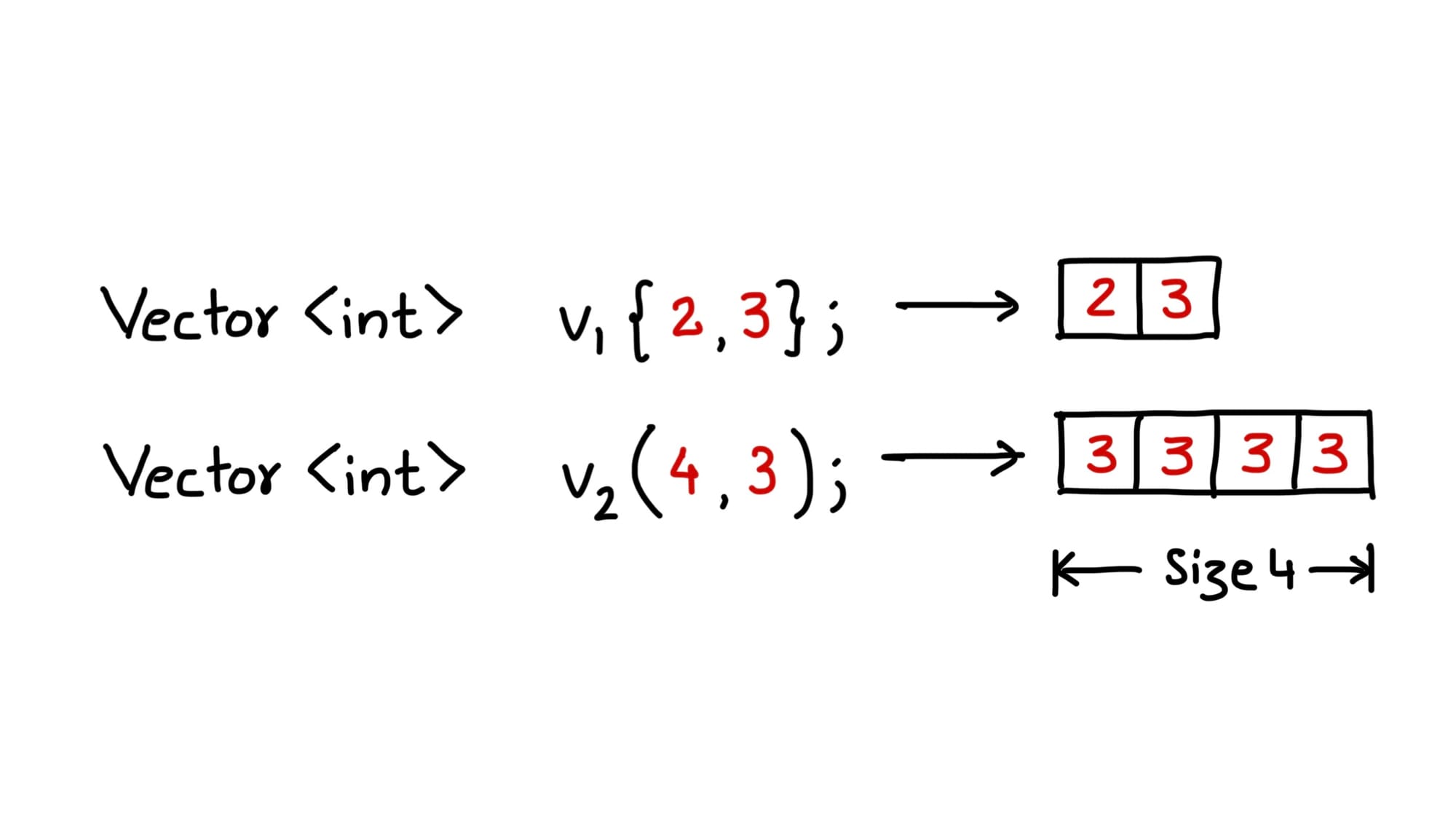
std::vector<int> vec2(10); // Vector of 10 integers, initialized to 0
std::vector<int> vec3(10, 5); // Vector of 10 integers, initialized to 5
std::vector<int> vec4 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // Vector initialized with list of integers
return 0;
}
Basic Operations on std::vector
Adding Elements
Elements can be added to the end of the vector using the push_back method:
vec1.push_back(1); // Adds 1 to the end of vec1
vec1.push_back(2); // Adds 2 to the end of vec1
Accessing Elements
Elements in a vector can be accessed using the [] operator or the at method:
int firstElement = vec4[0]; // Access first element (no bounds checking)
int secondElement = vec4.at(1); // Access second element (with bounds checking)
Removing Elements
Elements can be removed from the end of the vector using the pop_back method:
vec1.pop_back(); // Removes last element from vec1
Iterating Over Elements
You can use a range-based for loop or an iterator to iterate over the elements of a vector:
for (int value : vec4) {
std::cout << value << " ";
}
for (std::vector<int>::iterator it = vec4.begin(); it != vec4.end(); ++it) {
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
Advanced Operations on std::vector
Inserting Elements
You can insert elements at a specific position using the insert method:
std::vector<int> numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
numbers.insert(numbers.begin() + 2, 10); // Insert 10 at the 3rd position
Erasing Elements
Elements can be removed from a specific position using the erase method:
numbers.erase(numbers.begin() + 2); // Remove element at the 3rd position
Resizing the Vector
The resize method adjusts the size of the vector:
numbers.resize(3); // Resize vector to contain only 3 elements
numbers.resize(5, 100); // Resize vector to 5 elements, new elements initialized to 100
Clearing the Vector
The clear method removes all elements from the vector:
numbers.clear(); // Clear all elements
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
Avoid Using [] for Out-of-Bounds Access
Using the [] operator does not perform bounds checking, which can lead to undefined behavior. Use at for safer access:
try {
int value = numbers.at(10); // This will throw an exception if out of bounds
} catch (const std::out_of_range& e) {
std::cerr << "Out of range error: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
Reserve Capacity for Efficiency
If you know the approximate number of elements in advance, use reserve to allocate memory and avoid multiple reallocations:
numbers.reserve(100); // Allocate memory for 100 elements
Avoid Excessive Copies
When passing a vector to a function, use references to avoid copying:
void processVector(const std::vector<int>& vec) {
// Processing vector without copying
}
Conclusion
std::vector is a powerful and flexible container in C++ that allows you to manage dynamic collections of data efficiently. By understanding and utilizing the basic and advanced operations of std::vector, you can write more efficient and maintainable C++ programs. Whether you are managing a list of students, storing sensor data, or handling any dynamic array of elements, std::vector is an invaluable tool in your C++ toolkit.
Summary of Key Points
- Dynamic Size:
std::vectorcan grow and shrink as needed. - Memory Management: Automatically handles memory allocation and deallocation.
- Safe Access: Use
atfor bounds-checked access. - Performance: Contiguous memory allocation improves performance.
- Flexibility: Easily insert, erase, and resize elements.
By mastering std::vector, you will enhance your ability to handle dynamic data structures in C++, preparing you for more complex programming challenges. Happy coding!

Discussion