Why Do Arrays Start With Index Zero?
The Arrays in most programming languages(C, C++, Java, Python) start with index 0 instead of 1. While it may seem counterintuitive, but using zero-based indexing offers unexpected advantages for both compilers and programmers.
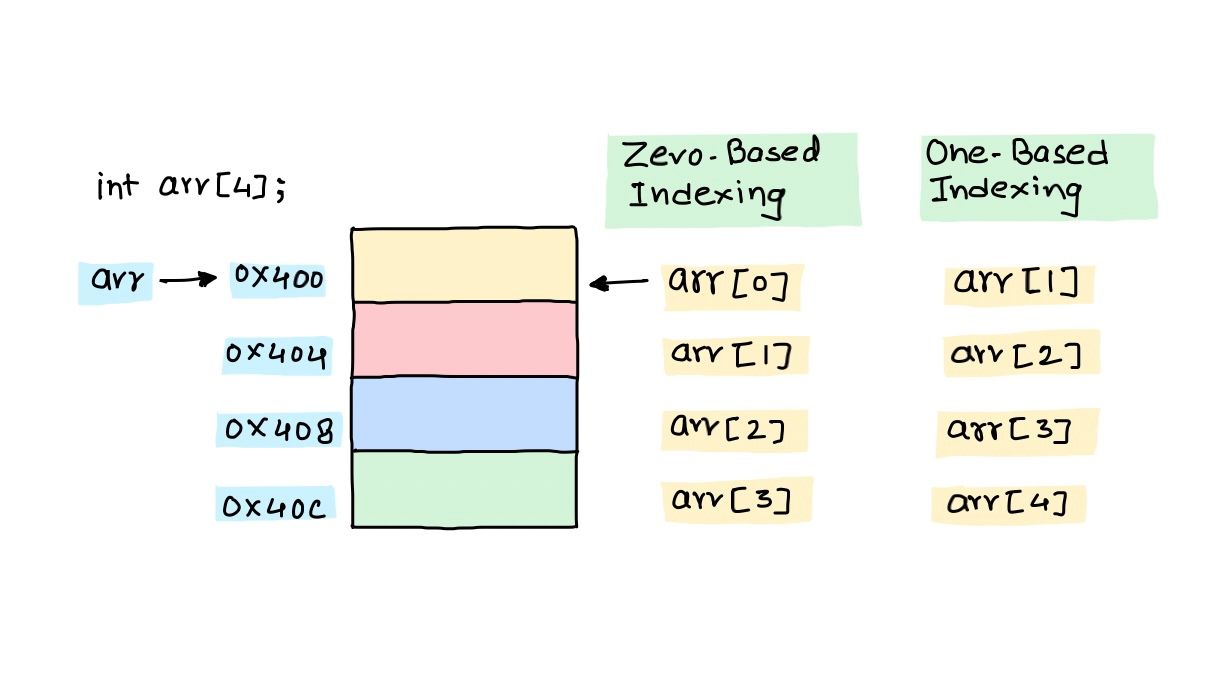
Recall the instance when you were introduced to the C programming language and were told that arrays in C start with index zero. I bet you wondered why 0! 🤔 Wouldn't be 1 a more obvious choice.
The Arrays in most programming languages(C, C++, Java, Python) start with index 0 instead of 1 and there are some surprising benefits of zero-based indexing for both compilers and programmers 😍.
Faster Compilation
In C, The name of an array is essentially a pointer to the starting address of contiguous memory allocated. Consider an array with starting address as 0x400.
int arr[5];In Zero Based Indexing
To access the first element in array, arr[0] must be computed as *(arr + 0). Similarly, To access ith element in array, arr[i] must be computed as *(arr + i * sizeof(int)). It takes compiler 2 add operations to compute the address of ith element.
In One Based Indexing
The first element in array, arr[1] must be computed as *(arr + 1 - 1). Similarly,ith element in array, arr[i] must be computed as *(arr + (i - 1) * sizeof(int)). It takes compiler 3 add operation to compute the address of ith element.
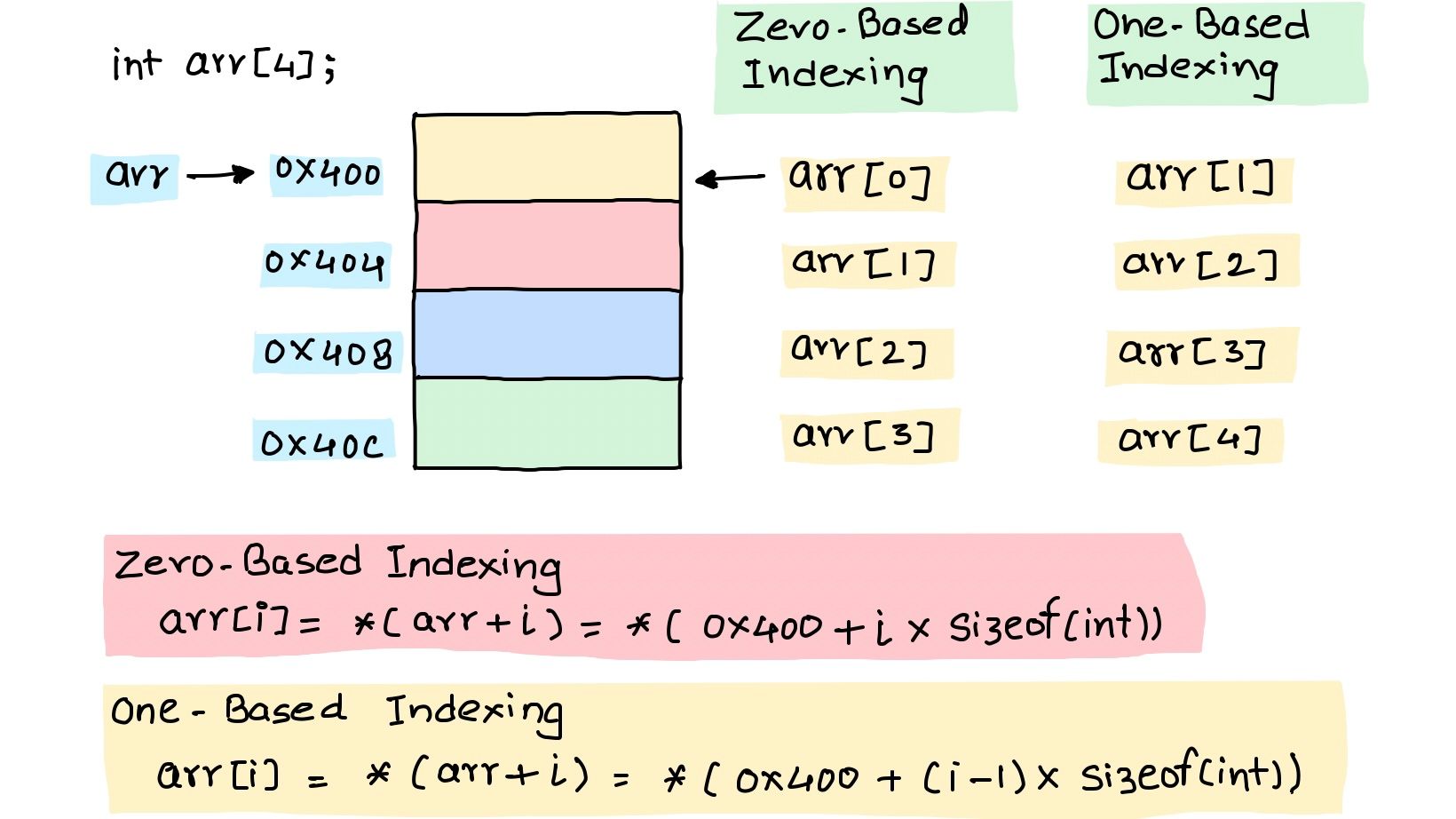
Hence, It is efficient for the compiler to implement zero-based indexing ✌️.
Now, How many operations does it take to compute the address of arr[i][j]? I will leave it to you as an exercise ☺️, please respond in the comment section.
Programmer's Ease
Let us say, we are implementing a hash table that maps each integer key to one of the N buckets. If our array of buckets is indexed starting at 0, we can write bucket = key mod n. But if it's indexed starting at 1, we will have to write bucket = (key mod n) + 1.
Above is one such example, but there could be many more examples where one has to explicitly add +1 or -1 in 1-based indexing, leading to more bugs 🐞 in the code.
A computer memory address also starts with 0 and grows to 2^N cells, where N is the number of bits used for addressing. What if it starts at 1?

If we start the memory address from 1, The extra bit is needed to access exactly 1 address(last cell), without the extra bit, the last cell will be inaccessible.
Conclusion 💯
We learned how the zero-based indexing in an array helps the compiler perform less operations and how it avoids programmers to deal with less math leading to fewer programming bugs.
Discussion